Author: Valentin Ionescu
Vol. 9 • No. 17 • 2024
• Impact on Capital Markets and Insurance Companies
The projected effects of Romania’s OECD entry on capital markets are estimated to enhance foreign investment, improve market efficiency, improve business information and introduce new financial instruments. Insurers would gain from higher consumer confidence and improved market growth possibilities, in particular cross-border growth.
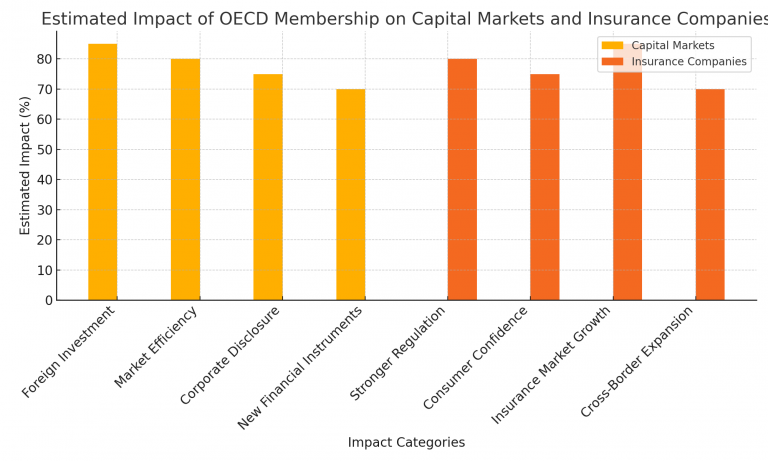
• Impact on Financial Services
With more rigorous regulatory standards in place, domestic and foreign investors would increase their confidence in the Romanian financial market, which could attract more investments. This is due to the fact that OECD membership is seen as a mark of trustworthiness and stability.
Romania would arguably gain from increased financial innovation as OECD standards encourage transparency, exchange of data and accountable use of financial technology (FinTech), thereby making financial markets more effective and accessible. The OECD advances frameworks that reinforce both financial education and consumer protection. By joining these, Romania would increase safeguards for citizens using financial services such as banking, insurance and pension funds.
• Impact on Corporate Governance
Corporate governance in Romania should be aligned with the OECD principles, which focus on openness, responsibility and equitable treatment of shareholders. Eventually, this would mean greater protection for minority investors and a more robust governance environment for companies. By implementing the OECD corporate governance framework, Romanian companies could see a reduction in mismanagement and conflicts of interest. This would boost overall business performance and competitiveness.
The OECD guidance calls for reinforcing the responsibilities of board of directors, thereby ensuring that they play a key role in overseeing management and protecting the interests of stakeholders, which could help avoid corporate scandals and improve decision-making.
Consolidated governance practices would strengthen investor confidence and access to international capital markets, increasing the ability of Romanian companies to develop and globally compete.
• Impact on Capital Markets
With OECD status indicating stability and compliance with international standards, Romanian capital markets are susceptible to an inflow of foreign capital. Institutional investors, are interested in markets with transparent governance rules and OECD membership could make Romania a safer and more trustworthy market.
Harmonization with OECD capital market standards would raise market efficiency by improving trading infrastructure, transparency and regulatory oversight. This could create more liquidity, making it easier for companies to raise capital through stock or bond offerings, and investors could trade securities with less risk of volatility or manipulation.
• Impact on Insurance Companies
While insurers continue to enhance their regulatory compliance with international standards, consumers would gain from stronger consumer protections, including better claims settlement processes, transparency in pricing and better oversight of how policies are sold. As a result, the take-up of insurance products by Romanian consumers could increase.
With reforms supported by the OECD, insurance penetration (the percentage of individuals and businesses using insurance services) is expected to increase. Enhancing the industry’s reputation and increasing consumer confidence could stimulate growth in life, health and property and casualty insurance.
Harmonized legislation could make it easier for Romanian insurance players to establish themselves in other OECD member countries. This could provide growth opportunities for local insurers while stimulating competition in the Romanian market from foreign insurers.
• Broader Effects on Both Capital Markets and Insurance
Capital markets and the insurance sector would both gain from enhanced risk management practices. For capital markets, this implies better governance and regulatory supervision, while for insurers, stricter risk-based capital requirements and stricter underwriting practices.
With stronger regulatory frameworks, these two sectors would lead to greater stability in the financial system, reducing the likelihood of crises caused by financial mismanagement. In short, OECD membership is expected to stimulate foreign investment, improve transparency and risk management in capital markets and the insurance sector in Romania. Those changes are expected to generate higher market confidence, growth in both sectors and a more resilient financial system in general.
• Romania versus OECD Average in Financial Services and Corporate Governance
A comparison of Romania’s current performance with the OECD average indicates potential gains that Romania could achieve by aligning its financial services and corporate governance frameworks with OECD standards.
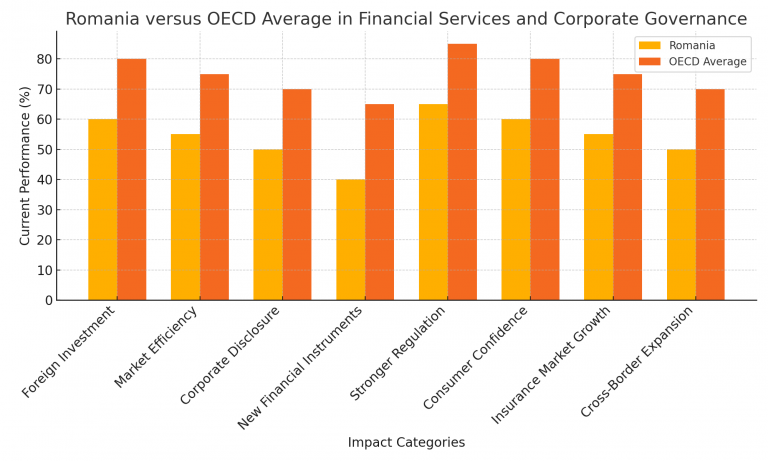
The comparison between Romania and the OECD average in key financial sectors and corporate governance highlights several key conclusions:
Through OECD membership, Romania could align its financial and governance standards with international best practices. This could lead to significant improvements in foreign investment inflows, stronger consumer protection, and the development of more sophisticated financial instruments.
Romania has relatively robust regulations in areas like insurance and corporate governance compared to other sectors. However, aligning more closely with OECD standards could help close market efficiency gaps and enhance overall economic stability.
Addressing these areas would boost Romania’s competitiveness, build investor confidence, and support sustainable long-term growth, positioning the country as a more integrated participant in the global economy.
Conclusions
OECD membership provides significant potential for growth and enhancement. Compliance with OECD norms could lead to stricter regulation, greater consumer confidence and increased market efficiency, ultimately making Romania a more competitive and attractive market for investment and growth. In short, the evidence illustrates that Romania could benefit significantly from OECD membership, with improvements in both capital markets and the insurance sector, moving closer to OECD benchmarks.
The analysis and conclusions are based on general knowledge of the OECD’s role in promoting economic stability, corporate governance and financial regulation.
References
[1] National Bank of Romania (2024). Financial Stability Report 2024.
[2] OECD (2023). Corporate Governance Factbook 2023. OECD Publishing.
[3] OECD (2024). Economic Surveys: Romania 2024, OECD Publishing.
[4] Romanian Financial Supervisory Authority (2024). Annual Report 2023.
[5] World Bank (2023). Romania Economic Update: Fall 2023. World Bank Group.
DOI: 10.55654/JFS.2024.9.17.14
